Introduction

In today’s digital world, simply creating a website isn’t enough — your content must be search engine optimized to reach the right audience. That’s where On-Page SEO plays a crucial role.
On-Page SEO refers to all the optimization techniques you apply within your website to help search engines understand your content and rank it higher. It’s the foundation of every strong SEO strategy and a must for anyone aiming to grow their online visibility.
What Is On-Page SEO?

On-Page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) involves optimizing individual web pages to improve their ranking and drive relevant traffic. Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on backlinks and external factors, on-page SEO focuses on content quality, structure, and technical elements within your site.
It ensures your website is both search engine-friendly and user-friendly.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?
Search engines like Google use complex algorithms to determine which pages deserve to rank at the top. On-page SEO helps you:
- Improve visibility: Search engines can easily understand your topic and relevance.
- Boost user experience: Visitors stay longer and interact more with your content.
- Increase conversions: Targeted visitors are more likely to become customers.
In short — strong on-page SEO = higher rankings + more traffic + better credibility.
Key Elements of On-Page SEO
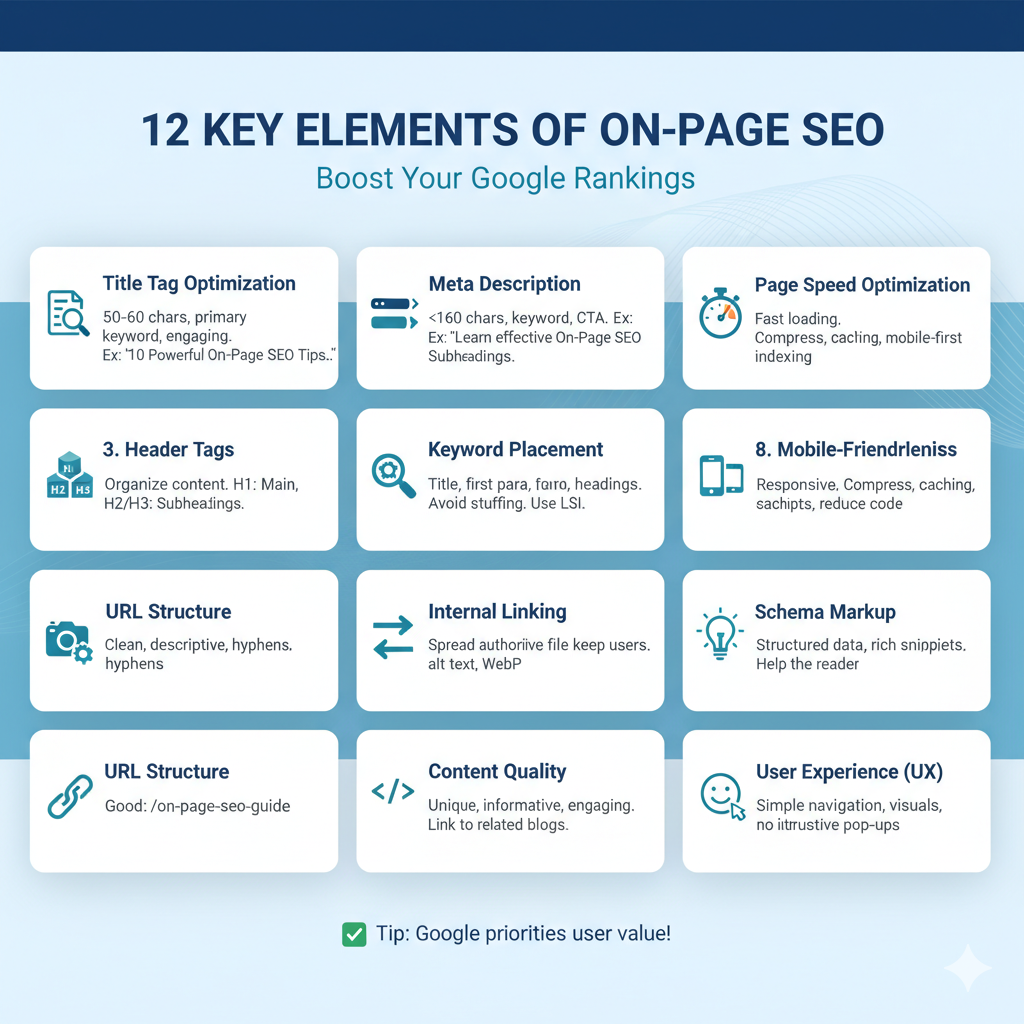
1. Title Tag Optimization
Your title tag is the first thing users see on Google. It should be:
- Between 50–60 characters long
- Include your primary keyword naturally
- Be engaging and relevant
Example:
Instead of “SEO Tips,” write “10 Powerful On-Page SEO Tips to Boost Your Google Rankings.”
2. Meta Description
The meta description summarizes your page content.
- Keep it under 160 characters
- Include your main keyword
- Add a call-to-action (CTA)
Example:
“Learn effective On-Page SEO strategies to boost your rankings and drive traffic. Start optimizing your website today!”
3. Header Tags (H1, H2, H3…)
Headers organize your content and make it easier to read.
- H1: Main title (use once per page)
- H2, H3: Subheadings to structure your content
Headers help both readers and search engines understand your page hierarchy.
4. URL Structure
A clean and keyword-rich URL helps users and search engines identify the topic quickly.
Good Example:www.example.com/on-page-seo-guide
Bad Example:www.example.com/?p=12345
✅ Tip: Keep URLs short, descriptive, and use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_).
5. Keyword Placement
Keywords are the backbone of SEO.
- Place your main keyword in the title, first paragraph, headings, and naturally throughout the text.
- Avoid keyword stuffing — focus on readability.
- Use LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords to support your main topic.
Example: For “On-Page SEO,” LSI keywords can include “SEO checklist,” “meta tags,” or “SEO optimization tips.”
6. Image Optimization
Images improve engagement but must be optimized for SEO:
- Compress images for faster loading.
- Use descriptive file names and alt text with relevant keywords.
- Use WebP format for better performance.
7. Internal Linking
Linking to other relevant pages on your site helps:
- Spread link authority
- Keep users on your site longer
- Help search engines discover more pages
Example:
If you’re writing about On-Page SEO, link to your blog about Off-Page SEO or Keyword Research.
8. Mobile-Friendliness
With mobile traffic dominating searches, your website must be responsive.
Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, so ensure your site loads well on all devices.
9. Page Speed Optimization
A slow site means poor user experience.
Improve loading times by:
- Compressing images
- Using caching plugins
- Reducing unnecessary code
- Choosing a fast hosting provider
You can check your site’s speed using Google PageSpeed Insights.
10. Content Quality and Readability
High-quality content is the most important part of On-Page SEO.
Your content should be:
- Unique and original
- Informative and engaging
- Structured with short paragraphs, bullet points, and visuals
The goal is to help the reader — not just rank in Google.
11. Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data that helps search engines display rich snippets (like reviews, FAQs, and ratings).
Adding schema can improve your click-through rate (CTR) and make your result stand out in search results.
12. User Experience (UX)
Google measures how users interact with your site — if they leave quickly, your ranking may drop.
To improve UX:
- Keep navigation simple
- Use engaging visuals
- Avoid intrusive pop-ups
On-Page SEO Checklist (Quick Summary)
| Element | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Title Tag | Include main keyword, under 60 characters |
| Meta Description | Under 160 characters, include keyword & CTA |
| URL | Short, clean, descriptive |
| Header Tags | Use H1 for title, H2/H3 for structure |
| Keywords | Use naturally in content |
| Images | Compress, add alt text |
| Internal Links | Add 2–3 relevant internal links |
| Mobile-Friendly | Ensure responsive design |
| Page Speed | Load under 3 seconds |
| Schema Markup | Add for better CTR |
Conclusion
On-Page SEO is the foundation of successful SEO strategy. Even the best backlinks won’t help if your website isn’t optimized internally.
By following these techniques — optimizing titles, content, images, and structure — you’ll create a site that’s both search engine-friendly and user-focused.
Start implementing these On-Page SEO practices today, and you’ll see noticeable improvements in your rankings, traffic, and overall online presence.